Amplifier Guide
Welcome to our guide on amplifiers, the key link between your audio source and speakers. Choosing the right amplifier is a crucial decision in setting up your sound system. With a variety of types and factors to consider, it can seem overwhelming. But don’t worry, drawing on our 40 years of experience, we’ll simplify the basics, explore different types, and help you understand the role of amplifiers in enhancing your audio experience.

Amplifiers are the brains of a great sound system. As the bridge between a source, ie turntable, CD player, streamer, etc, and the speakers, amplifiers have a vital job.
Every decision matters regarding your system, but the amplifier you go with will be one of your biggest. So, where do you start? What should you look for? Why do you need an amplifier in the first place? There are so many questions and things to know about these units, and we haven’t even mentioned that multiple types of amplifiers exist. There is good news! We’ve gathered a lot of knowledge and experience in over 40 years in the industry and created this guide to help. Here, we’ll cover what amplifiers do, the types you’ll come across, and some other basics for understanding amplifiers.
What Amplifiers Do
On the surface, amplifiers have a simple job. And okay, technically, they do, but how they do and how well they do that job is vital to the success of your sound system. The primary goal of any amplifier is to take the line-level signals from your other components and amplify them to speaker-level signals.
Unless they have an amp built-in, your speakers can't adequately express line-level audio signals, so your amplifier serves as an intermediary. Speakers need a strong signal to drive them; the bigger the speaker, the more power is necessary. When amplifiers receive the line-level signals, they add the watts required to drive the speakers.
A Point of Clarification
Some people may refer to audio amplifiers as power amplifiers. This is a general classification for any amplifier that drives a speaker (or other high-powered device). Power amplifiers will do as advertised. They can have multiple outputs, but their ultimate priority is boosting source signals to ensure your speakers get the strength of signal they need to operate.
How to Think About Amplifiers
One of the most important ways to think about amplifiers is how many channels they can handle. A channel refers to an independent audio signal path. Each channel can carry a separate audio signal, such as the left or right channel in a stereo system or the individual channels in a surround sound setup. The number of channels in an amplifier determines how many speakers or audio sources the amplifier can handle simultaneously.
Audio amplifiers are often categorized by their number of channels, and there are three primary types: mono, stereo, and multi-channel. Mono or monoblock amplifiers have only one channel and power a single speaker or subwoofer, while stereo amplifiers have two channels designed to power a pair of speakers. Multi-channel amplifiers have more than two channels and power multiple speakers in various configurations, such as 3-channel, 5-channel, 7-channel, etc.
Monoblock Amplifiers
Monoblock amplifiers are single-channel amplifiers designed to power a single speaker or speaker system. Each monoblock amplifier is dedicated to driving one specific speaker. Monoblock amplifiers are often used in high-end audio systems and home theaters, especially when dealing with demanding and power-hungry speakers. Having separate amplifiers for each speaker minimizes potential interference between channels, which can improve overall sound quality. These amplifiers drive large, high-performance speakers or subwoofers, providing ample power and control for enhanced audio reproduction.
Stereo Amplifiers
Stereo amplifiers are two-channel amplifiers designed to power a pair of speakers, usually the left and right speakers, in a stereo audio setup. They are commonly used in traditional two-channel audio systems, such as Hi-Fi setups, where accurate sound reproduction and left-right audio separation are crucial. Stereo amplifiers are the backbone of many home audio systems, providing the necessary power to drive bookshelf speakers, floor-standing speakers, or other audio components.
Multi-Channel Amplifiers
Multi-channel amplifiers have more than two channels and are used to power multiple speakers in various configurations. They are commonly found in surround sound systems, home theaters, and car audio setups, where separate channels are required to power each speaker. Common configurations for multi-channel amplifiers include 3-channel, 5-channel, 7-channel, and even 11-channel setups, depending on the complexity of the audio system and the number of speakers involved. Each amplifier type has unique advantages and is selected based on the specific audio system requirements and desired experience. The choice between monoblock, stereo, or multi-channel amplifiers depends on speaker configuration, room size, audio source components, and personal preferences for audio quality and immersion.
Other Considerations
The number of channels is essential with amplifiers, but learning how they are comprised, their classification, and what additional features or add-ons they have are necessary to understand their importance in a Hi-Fi audio system. These things will affect the sound of your audio, whether the amplifier gives it a distinctive warmth like with a tube amplifier or can connect wirelessly. Even additions like preamplifiers and digital-to-analog converters can come into play when considering amplifiers.
Components of an Audio Amplifier
An audio amplifier is an electronic device comprising several main components that produce high-quality sound. These components include the input stage, which receives the weak audio signal from the source and prepares it for amplification; the amplification stage, which is where the actual amplification of the audio signal takes place using transistors, tubes, or integrated circuits and boosts the signal to a level that can drive the speakers or headphones; the output stage, which is the final stage of the amplifier and is responsible for ensuring that the signal is clean and free from distortion; and the power supply, which provides the necessary power to the amplifier circuit for the amplification process and converts the AC power from the wall outlet into DC power that the amplifier can use.
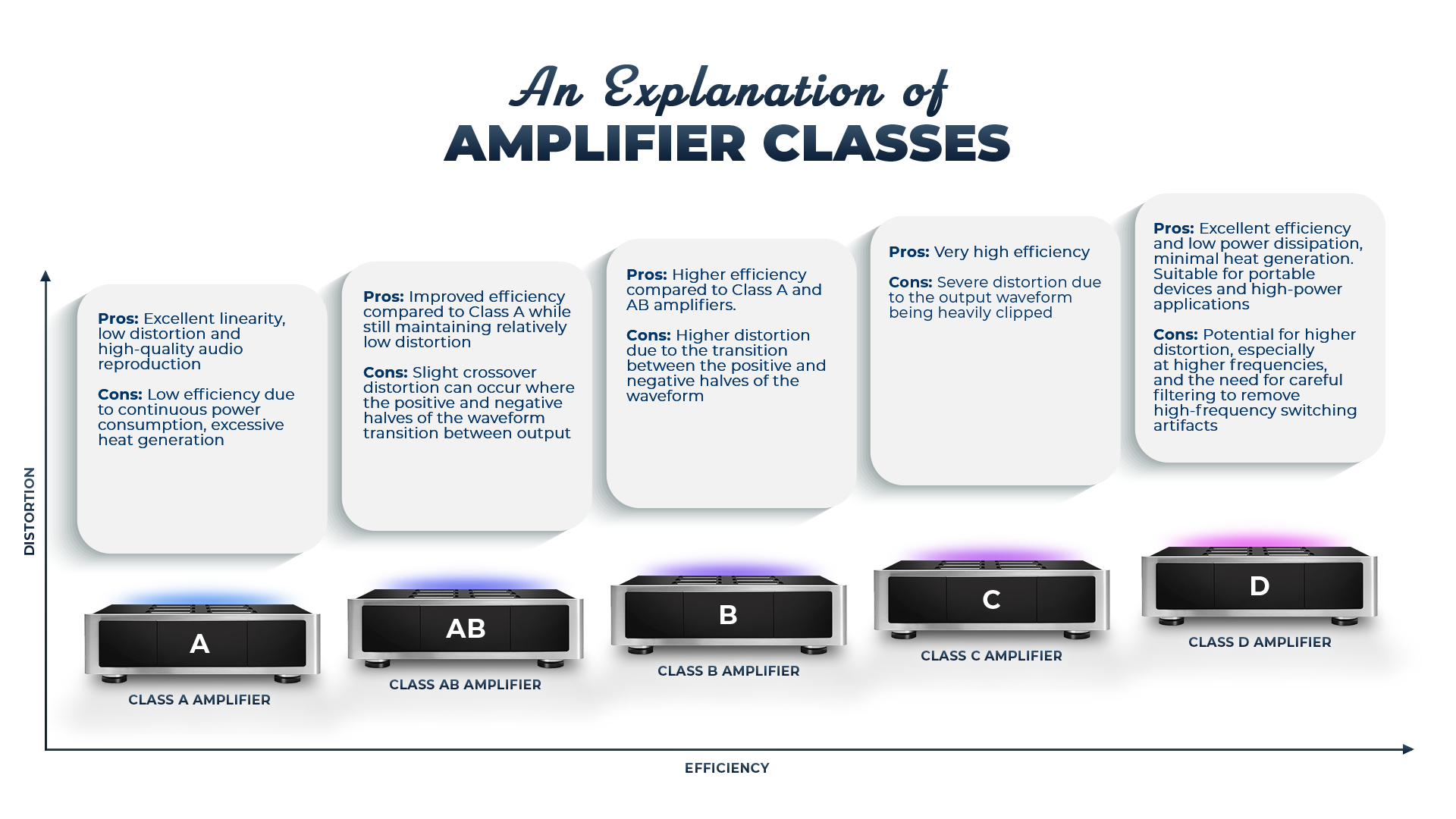
Amplifier Classifications
Amplifier classes refer to the method by which the amplifier operates and converts the input signal into an output signal. There are several classes of amplifiers, including Class A, Class AB, Class B, and Class D, among other less commonly known options, each with unique characteristics. Class A amplifiers are known for their high-quality sound output but have low efficiency and are unsuitable for high-power applications. Class B amplifiers are more efficient than Class A but have higher distortion levels. Amplifiers is the AB Class are a compromise between Class A and B. Class D amplifiers convert the input signal into pulses to achieve high efficiency. Understanding the differences between amplifier classes helps audiophiles choose an amplifier suitable to their system and listening preferences.
Tube vs Solid State
There are two different methods by which amplifiers do their jobs. The first way is tube amplifiers which use vacuum tubes to amplify the signal. They are known for providing a warm and natural sound with a smooth distortion that can be pleasing to the ear. However, they are often more expensive and require more maintenance than solid-state amplifiers. An example of a tube amplifier is the Rogue Audio Cronus Magnum III Integrated Amplifier. It produces sound by combining tubes
Solid-state amplifiers use transistors to amplify the signal. They are generally more reliable and have a more accurate and detailed sound than tube amplifiers. However, they can sometimes sound harsh or sterile compared to tube amplifiers. The NAD Masters M33 BluOS Streaming DAC Amplifier is a solid-state amplifier that uses advanced digital technology to deliver high-quality sound without tubes.
Amplifier Outputs
There are some key factors to consider regarding an amplifier’s connections. One of the most important considerations is the outputs that the amplifier provides. These can significantly enhance its versatility and functionality within a system’s overall design.
When selecting an amplifier, it is important to look for analog connections, such as RCA and XLR, which can accommodate balanced and unbalanced connections. These analog connections will provide greater flexibility and compatibility when interfacing with other components in your system. Additionally, looking for digital links, such as Toslink, coaxial, and USB, is important to ensure your amplifier can handle analog and digital signals.
By carefully considering your amplifier's available outputs, you can ensure your system is optimized for performance, compatibility, and versatility. This will enhance the quality of your sound and provide you with a more seamless and integrated audio experience overall.
Wireless Connectivity
Modern amplifiers, particularly integrated amplifiers, have recently introduced a plethora of exciting features. Among these is the inclusion of Wi-Fi/Bluetooth connectivity for your mobile devices and streamers. This addition lets you stream your favorite music and podcasts from your smartphone or tablet without additional hardware. Some amplifiers, like the remarkable HiFi Rose RS201E, even come with a built-in streamer, making it an all-in-one solution for your audio needs.
Moreover, if you have an older audio system that lacks wireless capability, integrating a new amplifier with Wi-Fi/Bluetooth connectivity can help you unlock a whole new world of audio possibilities. You can enjoy high-quality audio streaming from your favorite online services, such as Spotify, Apple Music, or Tidal, with just a touch of a button. The amplifier is the perfect stage for introducing new sources through wireless options.
Standalone vs Integrated Amplifiers
Now that we’ve gone over more about the types of amplifiers, we can dive into the debate that many audiophiles have. The choice between integrated and standalone units is heating up in the constantly changing world of Hi-Fi and audio technology. Both offer unique advantages and cater to specific audio setups and preferences. Some key distinctions remain between these two amplifier categories that can help you make an informed decision for your audio system.
Standalone Amplifiers
Standalone amplifiers, also known as separate amplifiers, are a popular choice among audio enthusiasts and professionals for several reasons:
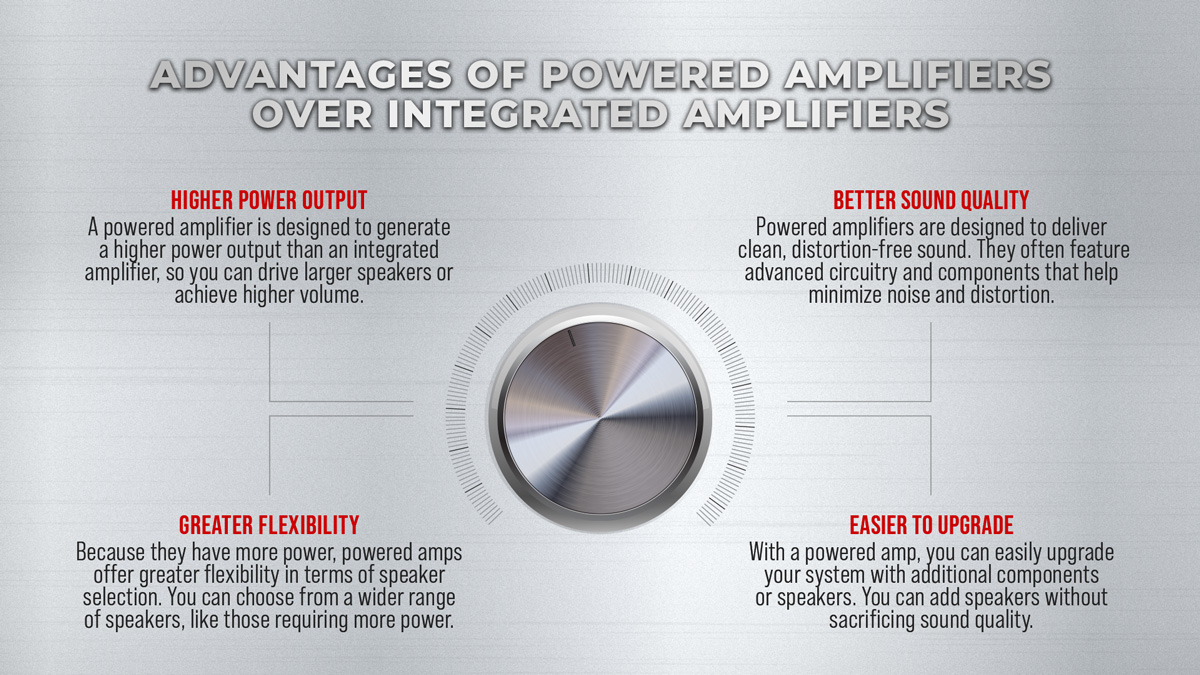
- Enhanced Performance: Designed specifically for amplification, standalone amplifiers deliver uncompromising performance with robust power supplies, high-quality components, and better cooling mechanisms, resulting in cleaner, more detailed, and dynamic sound reproduction.
- Flexibility and Customization: Standalone amplifiers allow mixing and matching components to suit individual preferences and specific audio setups, enabling audiophiles to create a tailor-made system for their needs.
- Power for Demanding Speakers: Standalone amplifiers are suitable for driving demanding or power-hungry speakers, ensuring ample headroom and better control over the speakers for improved clarity and transient response.
- Isolation from Interference: Separating the amplifier from other components reduces electrical interference and crosstalk between different audio system parts, contributing to cleaner audio signals and better signal-to-noise performance.
- Upgrade Path and Versatility: Standalone amplifiers can be easily upgraded or replaced without altering the entire audio system, allowing audiophiles to continuously refine and evolve their setups over time without requiring a complete system overhaul.
- Dedicated Amplification: Specialized solely for the amplification task, standalone amplifiers focus all their resources on delivering powerful, distortion-free signals to the speakers, resulting in improved efficiency and sound quality.
While standalone amplifiers require more investment and consideration than integrated amplifiers, they offer remarkable benefits for those who prefer power and customization possibilities.
Integrated Amplifiers
Integrated amplifiers, or all-in-one amplifiers, work similarly to standalone amplifiers but include a built-in preamplifier. The 2-in-1 package is undeniably a great deal and has, understandably, taken over as of late, with new features continuing to be added to this multifunctional component. These versatile audio components offer numerous benefits that make them popular choices for various audio setups:
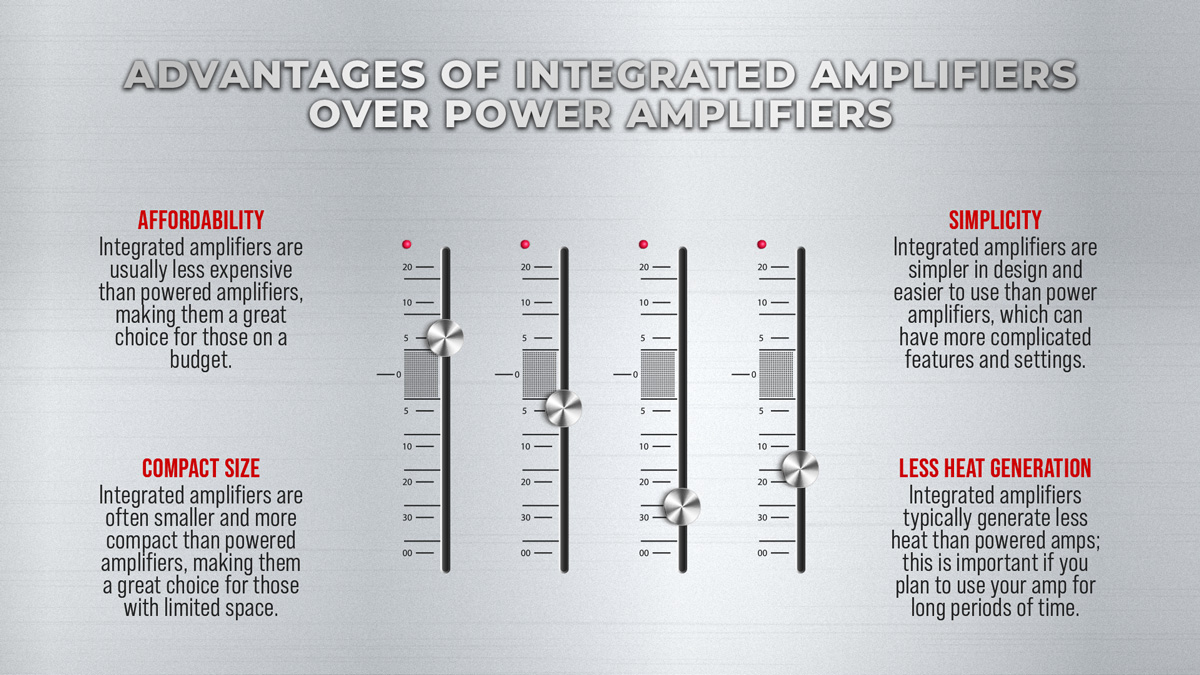
- Space-Saving and Convenience: Integrated amplifiers streamline the audio system by combining multiple functionalities into one unit. This compact design saves space and simplifies setup, making them ideal for those with limited space or seeking a straightforward solution.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Since integrated amplifiers house the preamp and power amp in one chassis, they often come at a more affordable price than individually purchasing separate preamplifiers and power amplifiers.
- Optimized Circuitry: With preamp and power amp sections designed together, integrated amplifiers offer optimized circuitry and signal paths. This synergy can lead to enhanced audio performance and reduced signal degradation.
- User-Friendly Controls: Integrated amplifiers typically have straightforward controls, including volume, balance, and tone adjustments, allowing users to fine-tune the sound output without complexity.
- Consistent Sound Signature: Since the preamp and power amp sections are designed to work in tandem, integrated amplifiers often produce a consistent sound signature, ensuring a coherent and harmonious listening experience.
- Versatility and Connectivity: Many modern integrated amplifiers include various connectivity options, such as Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and digital inputs, expanding their versatility and compatibility with a wide range of audio devices.
While integrated amplifiers may not offer the same level of customization and power as standalone amplifiers, their user-friendly design, affordability, and harmonious integration make them an excellent choice for audiophiles seeking a well-rounded and hassle-free audio experience. Whether setting up a basic stereo system or a compact home theater, integrated amplifiers cater to entry-level enthusiasts and seasoned listeners seeking simplicity without compromising audio quality.
Digital-to-Analog Converters
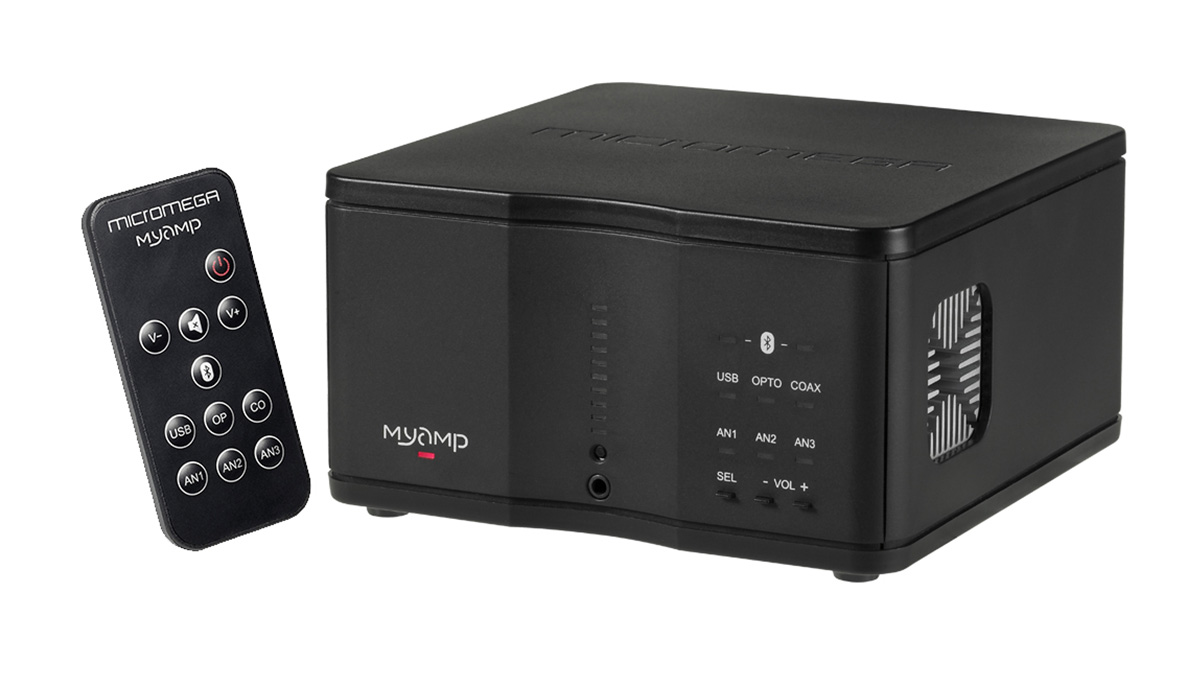
This is relatively uncommon, but some amps include a built-in DAC or digital-to-analog converter. If you want to condense your system as much as possible, an amp such as the Micromega MyAmp is an amplifier, DAC, and Bluetooth receiver all rolled into one convenient package. Of course, be wary of the potential issues or sacrifices to quality that come with that much functionality.
Finding Your Next Amplifier
Powered or integrated amplifiers are typically the heart of your system. Whatever your budget, ensure you're investing at the top. There's no shortage of options for those looking to upgrade or start from scratch; remember your needs, as that matters most. Also, check out customer reviews whenever you can; sound, especially at the Hi-Fi level, can be subjective. Listening to others' experiences is a great way to determine what's right for you. Whether you need tons of functionality or specialized power, get an amp that works with your system and, more importantly, your ears. If you still have questions about what amplifiers work best with your system or want to learn more, talk to one of our audio experts!